
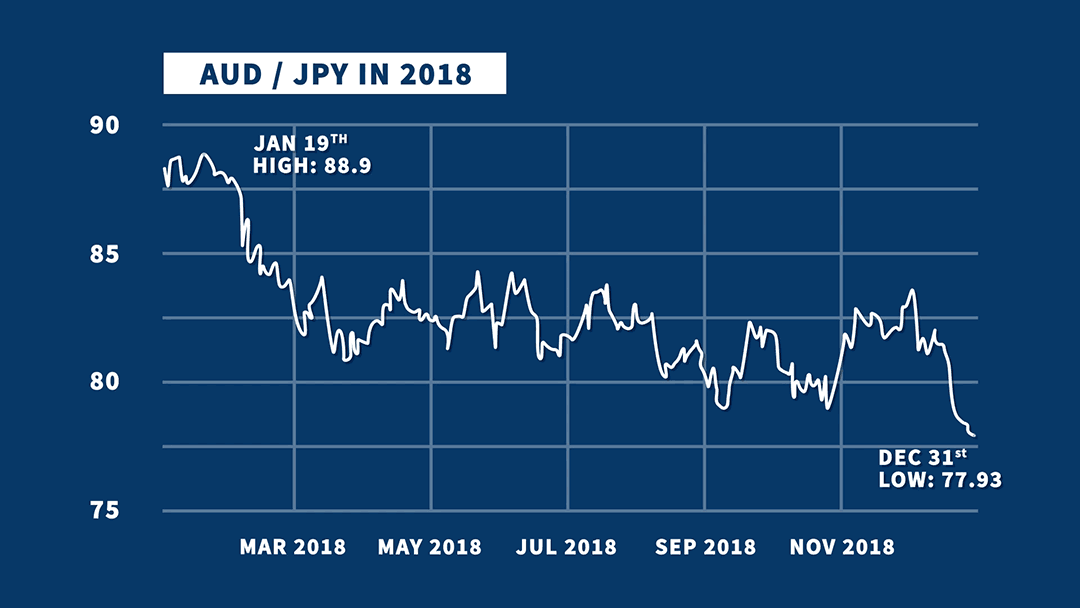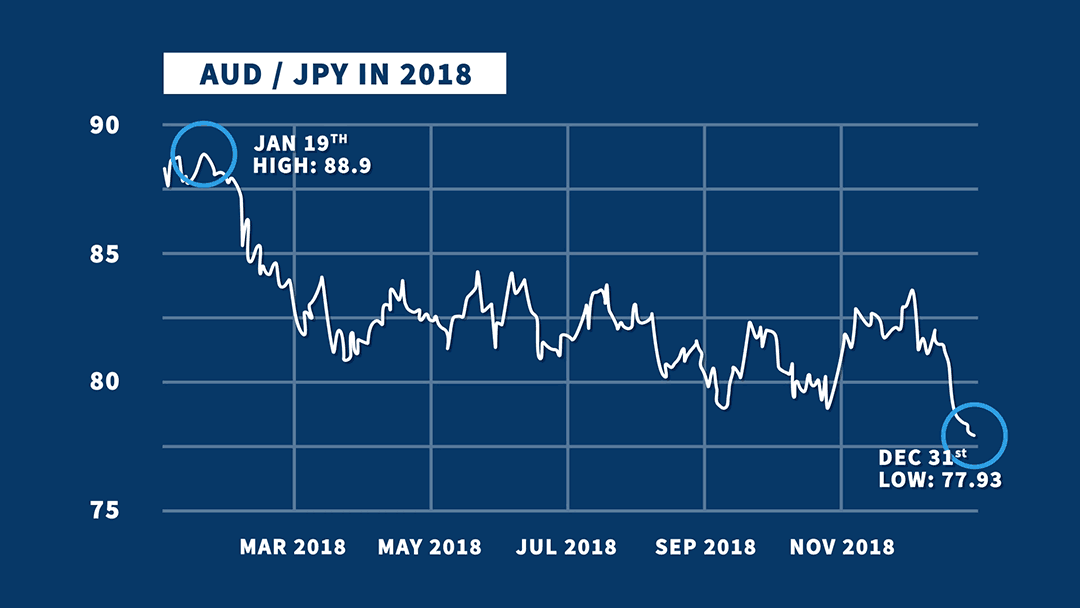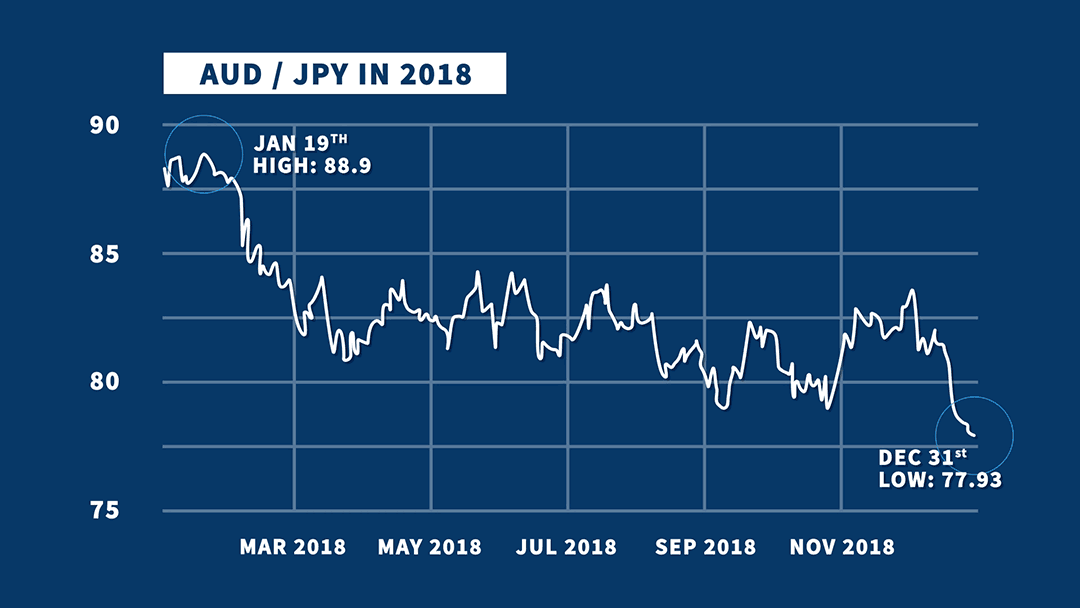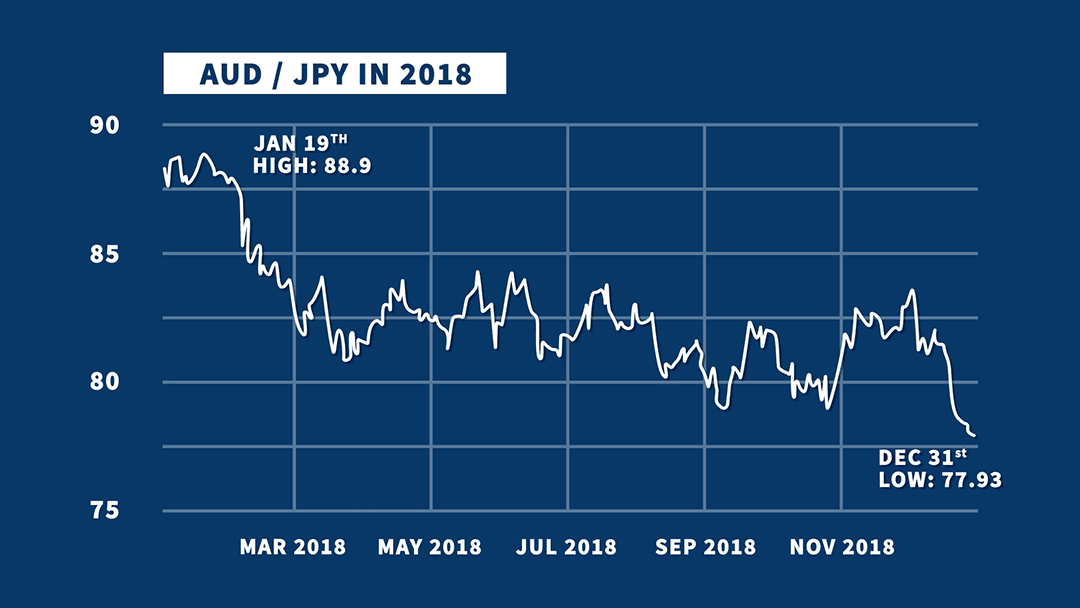
In order to determine which is the fixed currency when neither currency is on the above list (i.e. In some areas of Europe and in the retail market in the United Kingdom, EUR and GBP are reversed so that GBP is quoted as the fixed currency to the euro. For example, in a conversion from EUR to AUD, EUR is the fixed currency, AUD is the variable currency and the exchange rate indicates how many Australian dollars would be paid or received for 1 euro.
There is a market convention that rules the notation used to communicate the fixed and variable currencies in a quotation. On the other hand, cash is available for resale immediately, but incurs security, storage, and transportation costs, and the cost of tying up capital in a stock of banknotes (bills). The higher rate on documentary transactions has been justified as compensating for the additional time and cost of clearing the document. Different rates may also be quoted for cash, a documentary transaction or for electronic transfers. The quoted rates will incorporate an allowance for a dealer's margin (or profit) in trading, or else the margin may be recovered in the form of a commission or in some other way. The buying rate is the rate at which money dealers will buy foreign currency, and the selling rate is the rate at which they will sell that currency. Most trades are to or from the local currency. In the retail currency exchange market, different buying and selling rates will be quoted by money dealers. The spot exchange rate is the current exchange rate, while the forward exchange rate is an exchange rate that is quoted and traded today but for delivery and payment on a specific future date. trading from 20:15 GMT on Sunday until 22:00 GMT Friday). In floating exchange rate regimes, exchange rates are determined in the foreign exchange market, which is open to a wide range of different types of buyers and sellers, and where currency trading is continuous: 24 hours a day except weekends (i.e. Rather, national exchange rate regimes reflect political considerations.
#Japanese currency exchange rates free#
There is no agreement in the economic literature on the optimal national exchange rate (unlike on the subject of trade where free trade is considered optimal). Countries can also have a strong or weak currency. Governments can impose certain limits and controls on exchange rates. For example, a currency may be floating, pegged (fixed), or a hybrid. In this case it is said that the price of a dollar in relation to yen is ¥114, or equivalently that the price of a yen in relation to dollars is $1/114.Įach country determines the exchange rate regime that will apply to its currency. For example, an interbank exchange rate of 114 Japanese yen to the United States dollar means that ¥114 will be exchanged for US$1 or that US$1 will be exchanged for ¥114. The exchange rate is also regarded as the value of one country's currency in relation to another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of the euro. In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
